Last modified: December 10, 2025
Fullscript Assist
Providers
More data shouldn’t mean more work. Fullscript Assist is your plan-writing partner — centralizing the information you need to make clinical decisions, highlighting key insights from patient data, and making research more convenient.
Fullscript Assist can help you:
- Improve patient safety by catching potential interactions in real time.
- Make informed decisions faster with severity ratings and research-backed alerts.
- Stay in workflow — no need to leave the platform for clinical research.
- Support whole person care with tools that consider the full patient context.
Use the Fullscript Assist tool in conjunction with other features like smart product comparisons, similar products, ingredient intake summary, and currently taking to create plans the effectively and efficiently support patient wellness.
Accessing Fullscript Assist
You can open Fullscript Assist from the top-right corner of all pages in the Fullscript
platform.
Checking for interactions
Checking for interactions between different supplements, pharmaceuticals, and other wellness products.
After opening Fullscript Assist:
- Click Interaction checker.
- Select a pharmaceutical or supplement ingredient. If what you’re looking for isn’t in the initial list, use the search bar to find it.
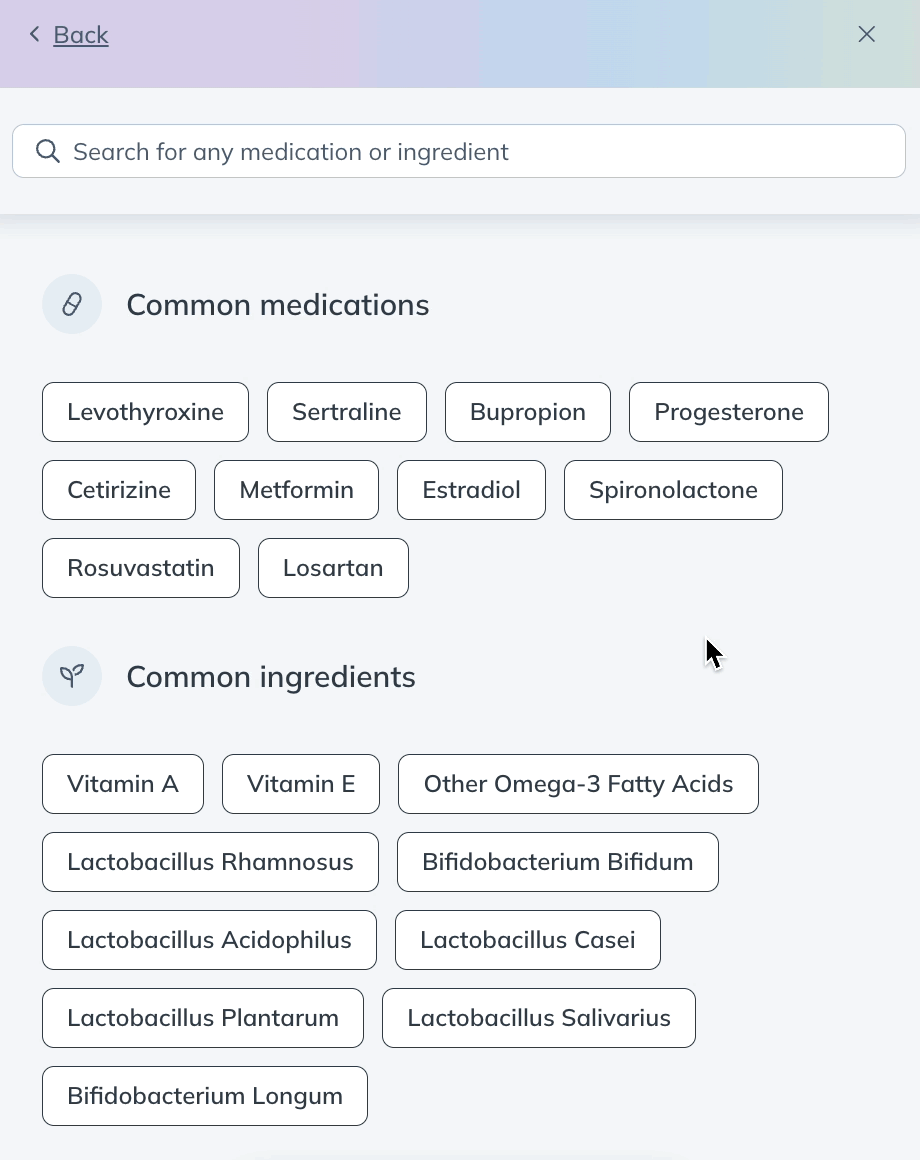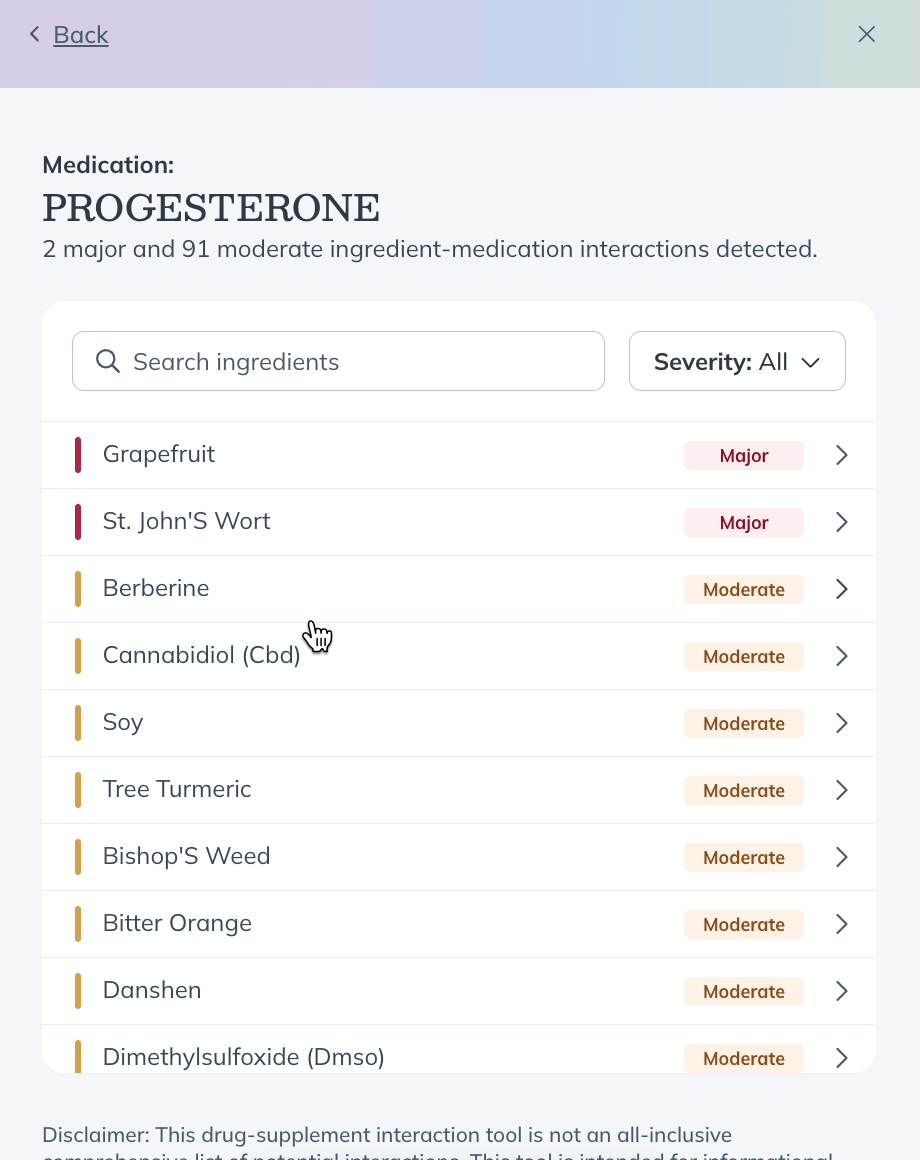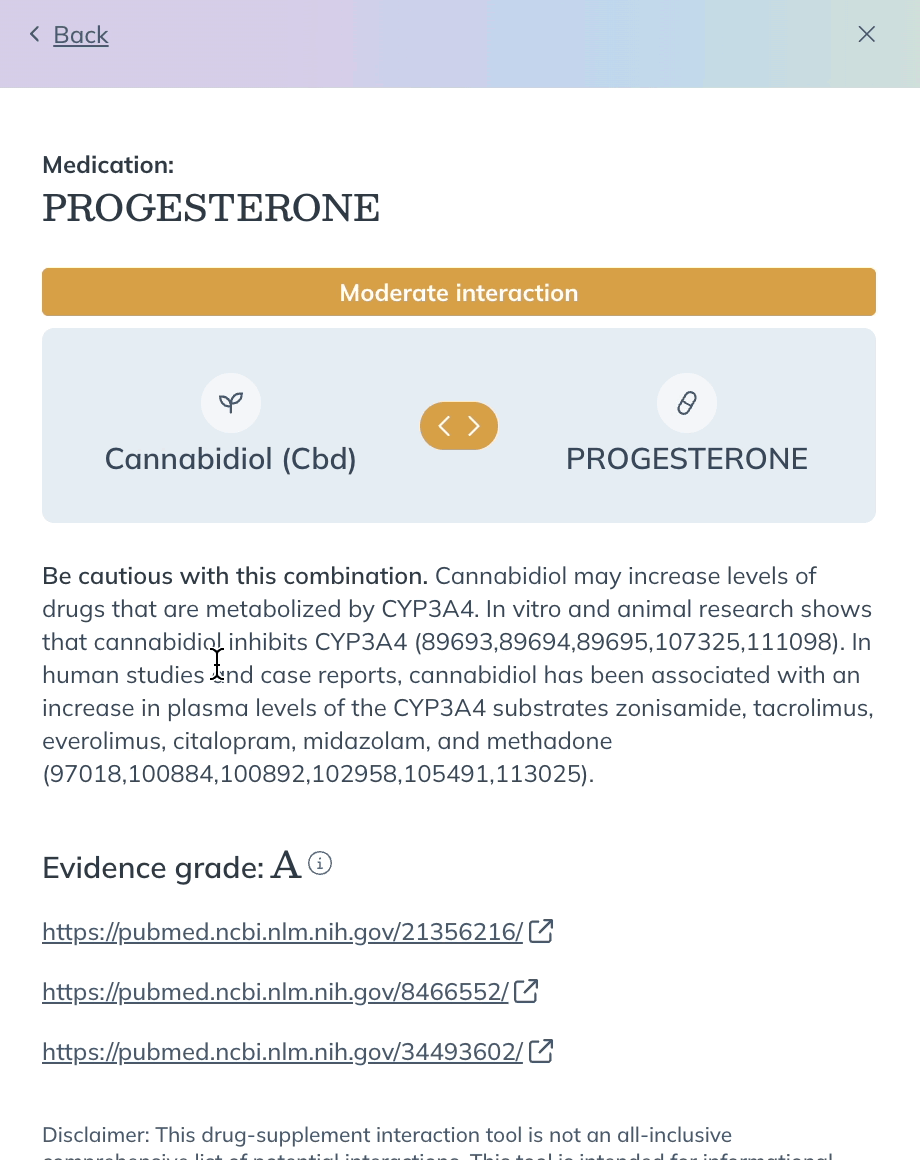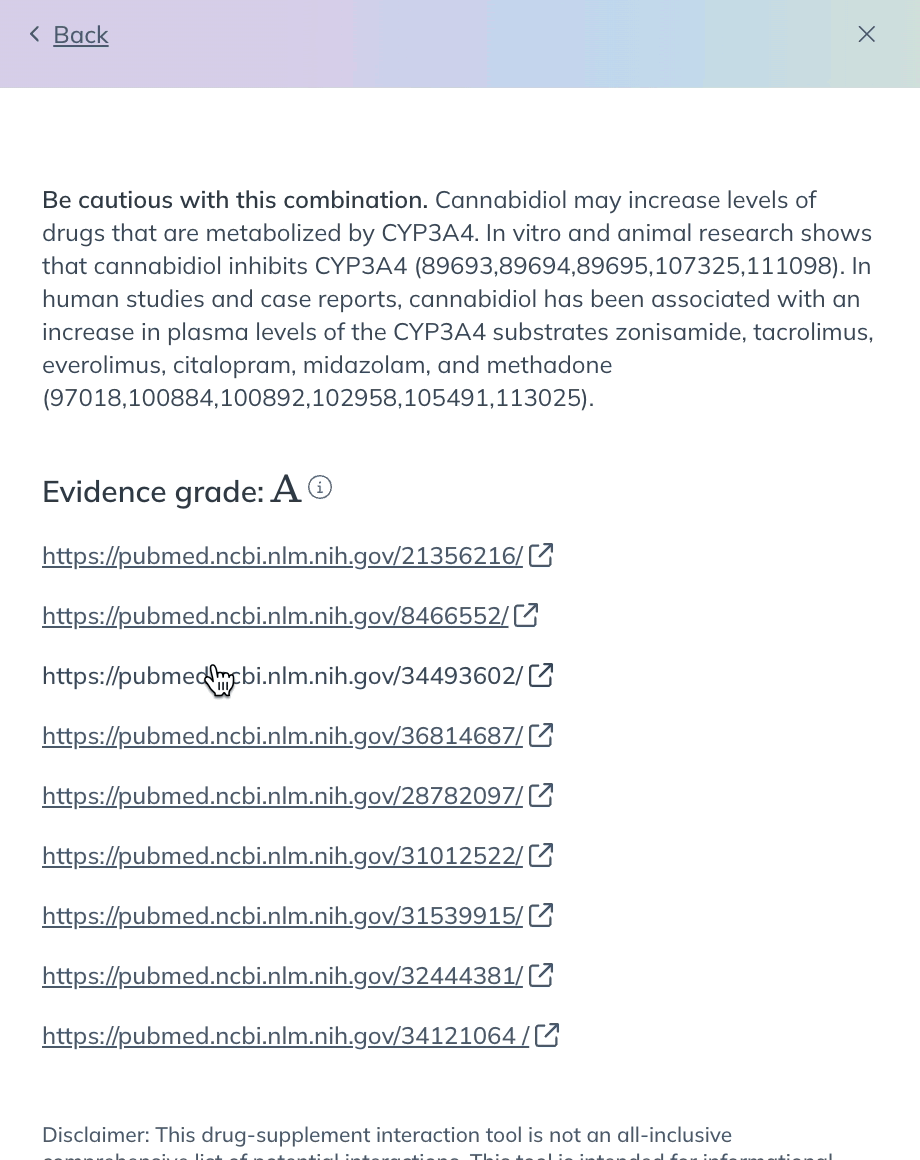
- After selecting a product, you’ll see a list of products that have a known interaction with it. Click a product in the list to learn more about how it interacts with your initial suggestion.
Nutrient depletion checker
The Depletion checker is a built-in clinical decision support feature that helps providers identify and address nutrient deficiencies caused by medications.
When a patient’s currently taking list includes medications, Fullscript automatically flags any potential nutrient depletions in the plan-writing workflow. These insights help you:
- See which nutrients may be depleted based on a patient’s reported medications.
- Understand the severity and level of supporting evidence behind each depletion.
- Search depletion risks by medication name when building templates or conducting research.
- Take action directly by creating supplement plans to address the deficiency.
Insights are pulled from pubmed and reviewed under Fullscript’s Evidence-Based Decision Support framework. Each result includes a severity rating, evidence grade, and access to supporting clinical references — helping you make informed care decisions, faster.
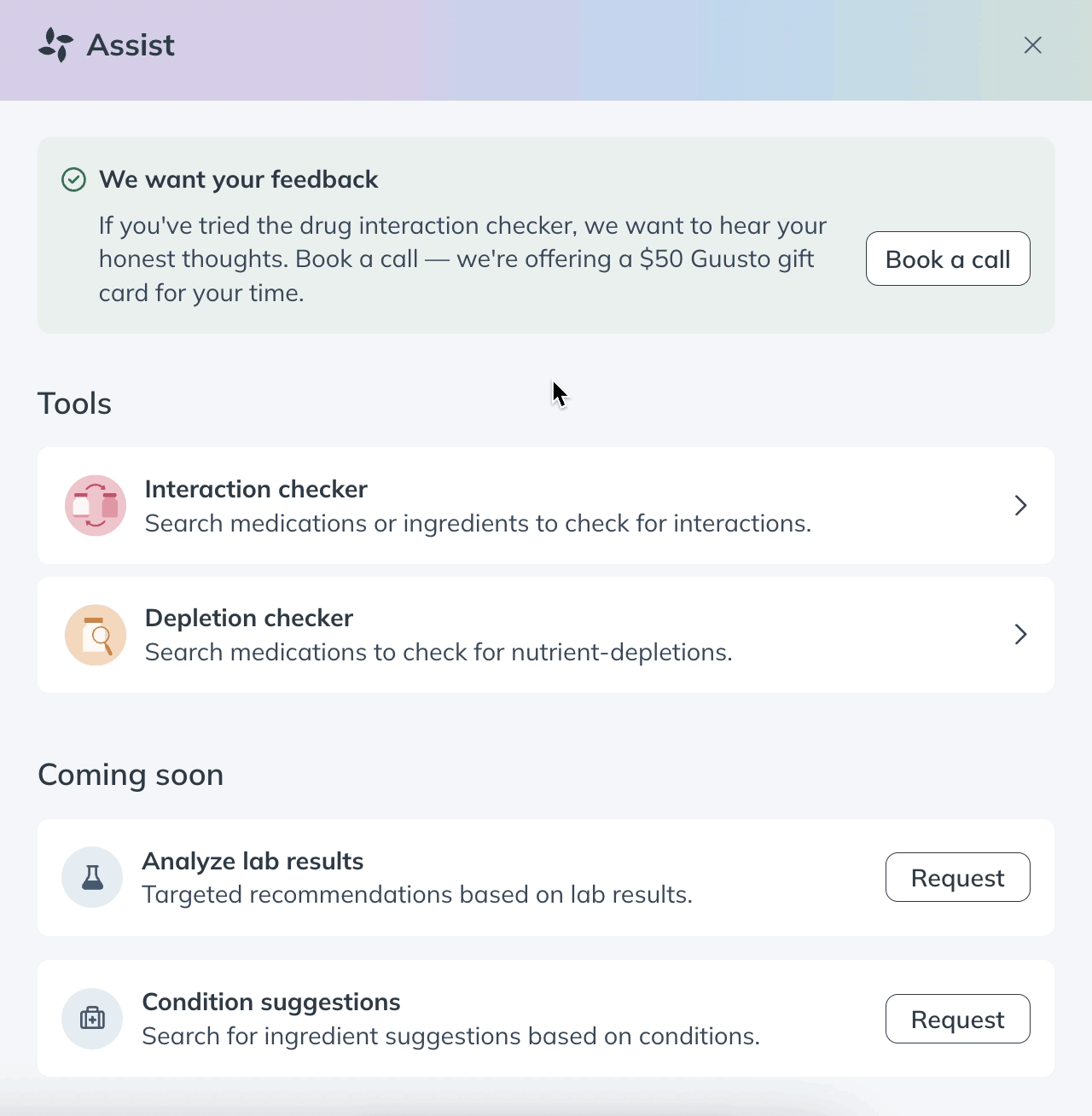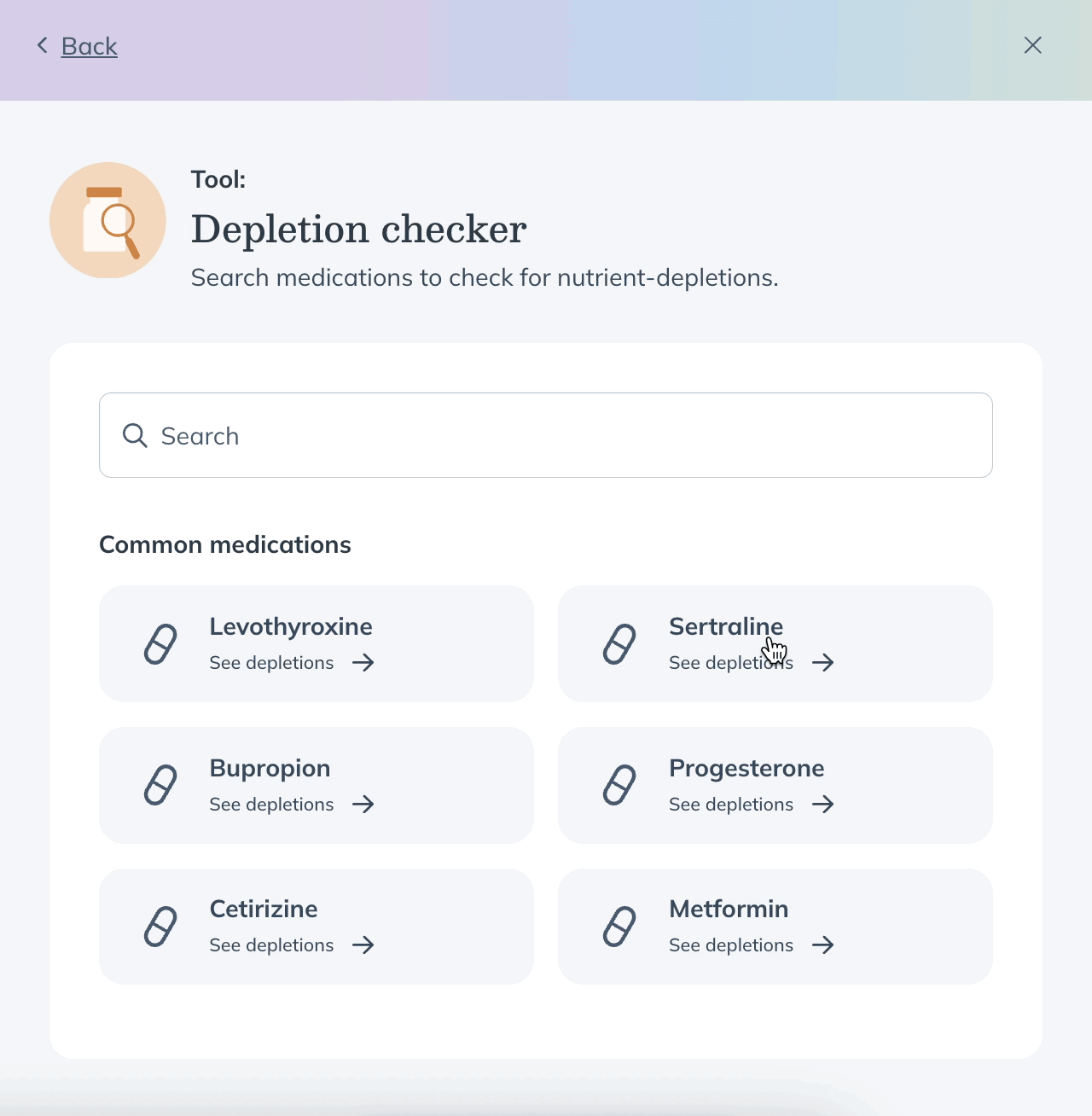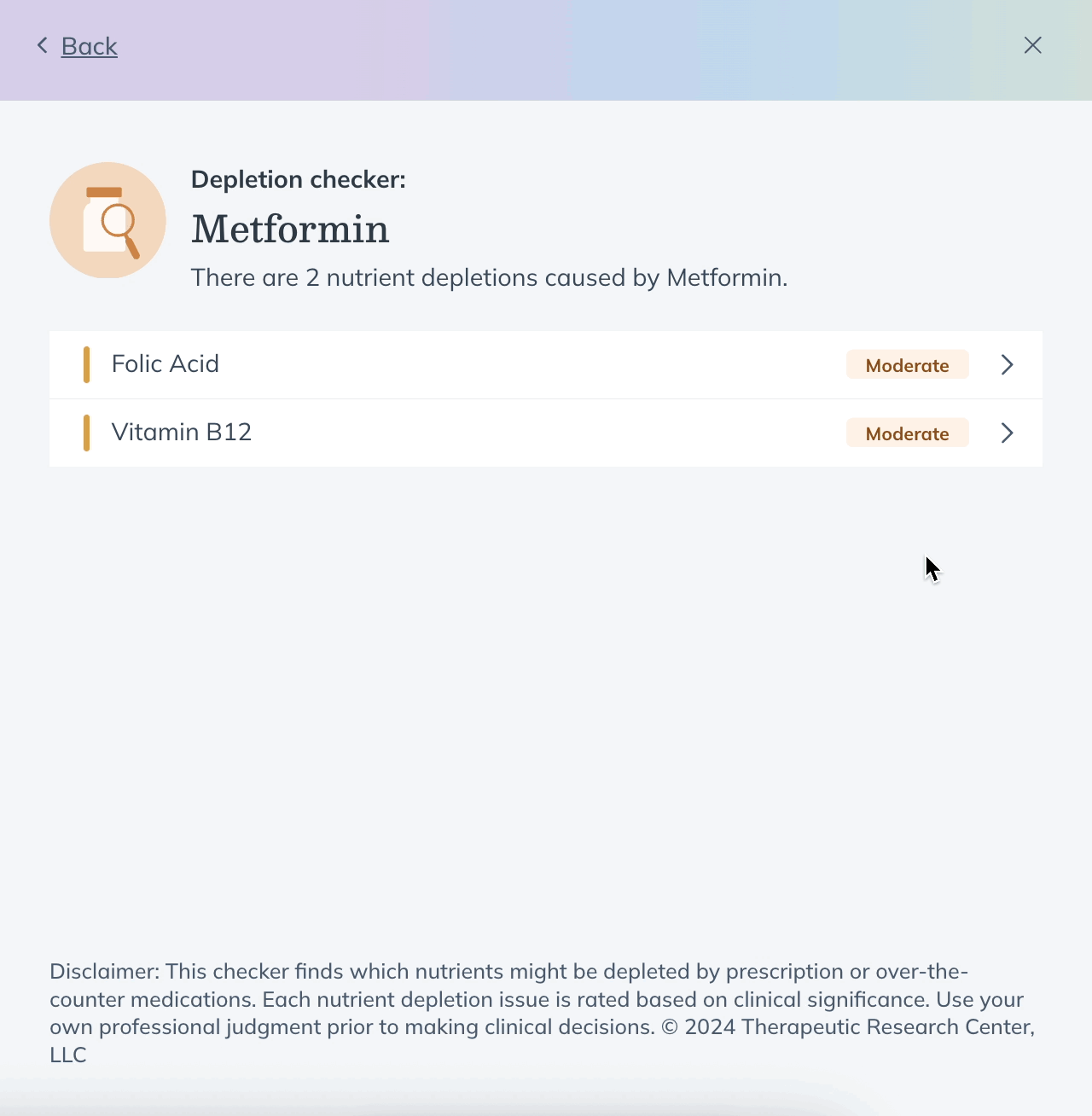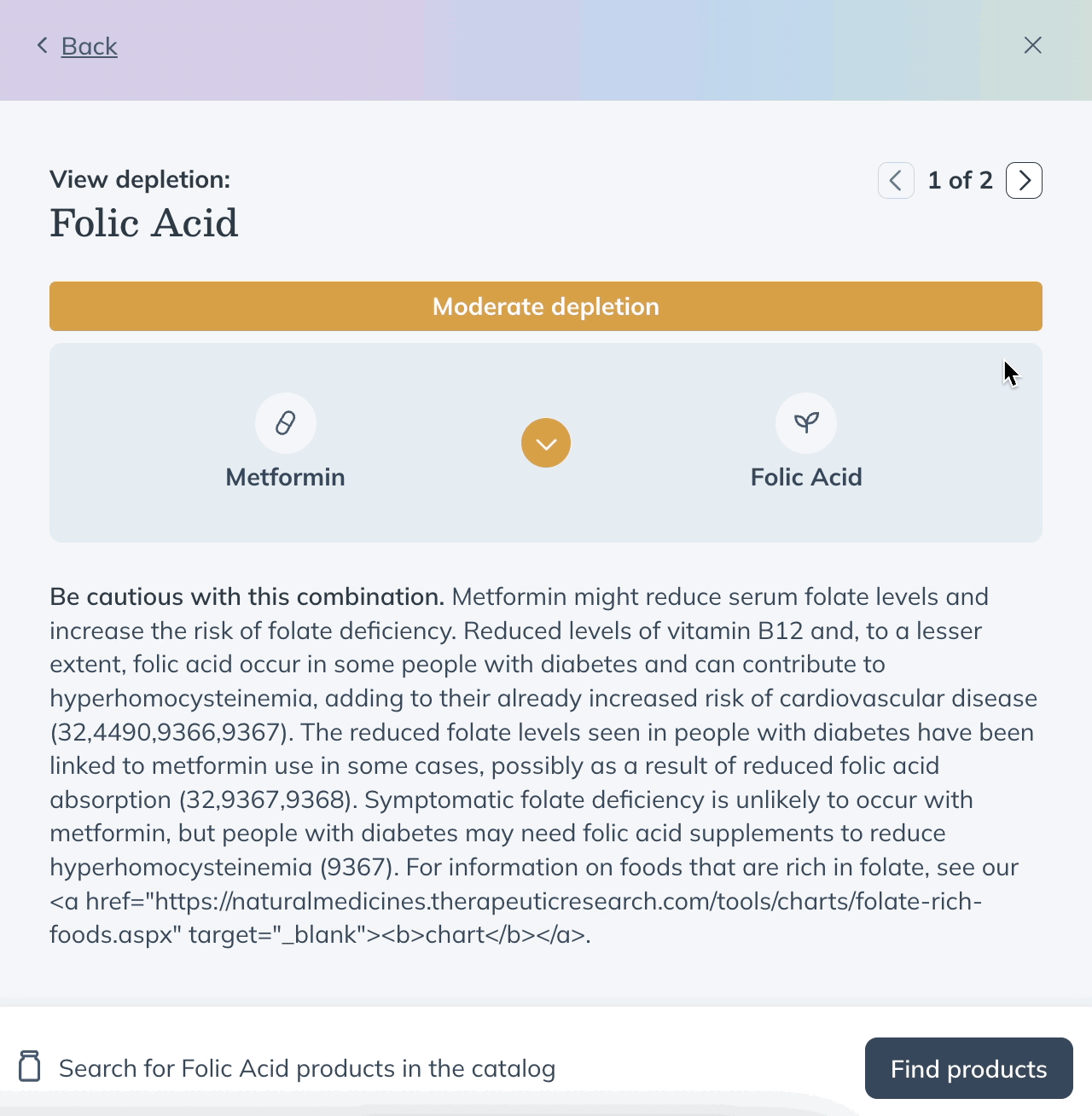
After opening Fullscript Assist:
- Click Depletion checker.
- Click on a common medication, or search for a medication you’re researching.
- You’ll see a list of nutrients that may be depleted by that medication. For more information, click the nutrient name.
Biomarker and condition insights (US-only)
Condition-based insights help you turn lab results or suspected conditions into clear, evidence-based insights within your plan-writing workflow. Bringing together biomarker interpretation, condition guidance, and supplement ingredients, it reduces reliance on fragmented resources or reference tools and saves time — without replacing clinical expertise.
With this tool, you can:
- Start with a patient’s lab results in Fullscript, then open Assist to view insights.
- Browse the built-in biomarker and condition reference guide without patient data.
- Review potential conditions grouped by health area, making lab interpretation easier and more actionable.
- For each condition, view ingredient suggestions with:
- A summary of supporting clinical evidence.
- Direct links to PubMed studies.
- A summary of supporting clinical evidence.
- From ingredient suggestions, jump directly into the Fullscript catalog to view relevant products (with filters for form, certifications, and allergens).

Reviewing potential conditions.